Diabetic Retinopathy
Eye Conditions
Cataract
CSCR
Diabetic Retinopathy
Epiretinal Membrane
Flashes and Floaters
Glaucoma
Macular Degeneration
Macular Hole
Retinal Detachment
Retinal Vein Occlusion
Uveitis
Vitreomacular Traction
Investigations
Procedures
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in the working age population. It causes vision loss through macular swelling, damage of the macula from lack of blood flow, internal bleeding in the eye and retinal detachment.

Macular swelling
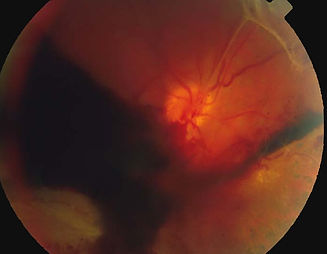
Vitreous haemorrhage
Even with treatment, diabetic patients have higher blood glucose level compared to non-diabetic individuals. Long-term exposure of blood vessels to higher glucose level causes damage. Initially, the blood vessels become leaky, leading to retinal swelling, bleeding and deposition of lipids in the retina. Further damage results in blockage of blood vessels. This reduces blood flow and the affected parts of the retina is irreversibly damaged.
Ultimately, diabetic retinopathy can cause blindness through scarring and detachment of the retina. It can also cause blindness through painful rubeotic glaucoma.
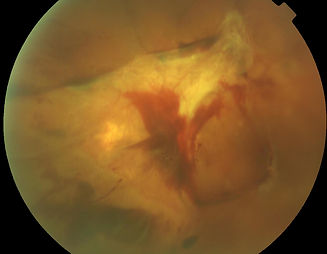
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
Laser therapy is used to treat macular swelling and to prevent complications of ischaemia (damage due to lack of blood flow).

Macular oedema
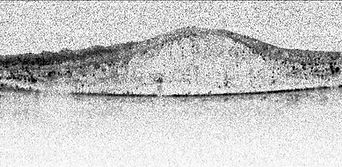
Intraocular injections have become the main treatment of macular oedema.
Anti-VEGF agents are most commonly used, but steroid injections are also effective.
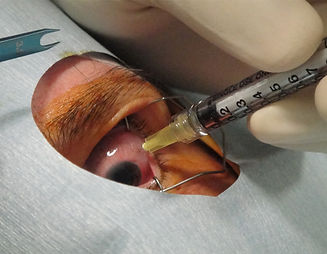
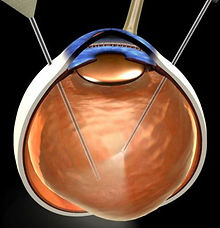
Vitrectomy may be required for persistent vitreous haemorrhage or retinal scarring and detachment.
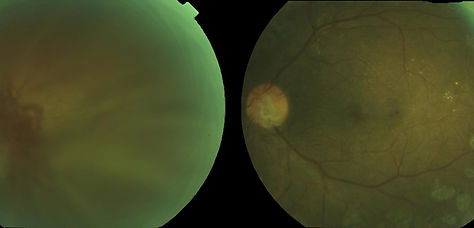
Before Surgery
After Surgery